
They then relax, so the heart can fill with blood again. When the heart beats normally, its muscular walls contract (tighten and squeeze) to force blood out and around the body.

Comply with archiving policies – you can deposit any version of your paper in any required repository or archive, and post articles on your personal or institutional website.Post-publication statistics – metrics shown with each article make it easy to check how often your paper is being downloaded via UJMS's website and how often it is being mentioned and shared through social media.Indexing – once published, your article will be comprehensively indexed in the foremost international databases.Impact Factor – The 2022 Impact Factor as announced by Clarivate Analytics, is 3.4.
#PAROXYSMAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ECG FREE#
Retain copyright – you retain copyright to your article and are free to disseminate it, make copies, deposit it in any repository, and more.Open access – UJMS publishes your work free from all access barriers, allowing for global distribution and more citations.WHY PUBLISH WITH Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences? A positive screening was highly predictive of AF in ECG during the follow-up.

In the subgroup with positive screening, 46.3% had AF compared with 6.7% in the subgroup with negative screening ( P < 0.0001).Ĭonclusions: The two screening approaches had a similar yield of arrhythmia, in spite of the group with intermittent monitoring having a more favorable clinical profile. During follow-up of 32 months, AF in 12-lead ECG was found in 7.0%. Results: AF was detected in 7.1% by continuous screening and in 5.1% by intermittent screening ( P = 0.3).
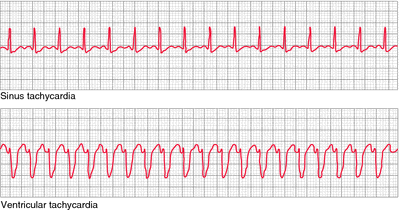
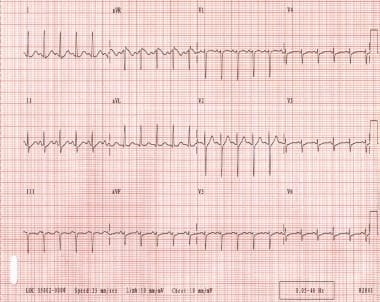
For comparison, we used an age- and sex-matched population with no known cerebrovascular event and a population with a cerebrovascular event that was not screened. Their clinical profile and vital status during the follow-up were obtained from the Swedish Stroke Register and the Swedish general population registry. Methods: The patients were identified in the local database of cardiovascular investigations. We related the result to subsequent occurrence of AF as detected in 12-lead ECG recordings. In a retrospective cohort study on 994 patients with an ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA), we have compared continuous 7-day monitoring to intermittent recording 60 sec three times daily with a handheld device during 3 weeks. Their relative efficiency is a matter of discussion. The method used is continuous electrocardiogram (ECG)-monitoring or multiple short ECG-recordings during an extended period. Background: The detection of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) is of importance in stroke care.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
